gopool - 字节跳动开源的Golang协程池速览
goroutine做为 golang中的轻量级线程实现,官方并没有提供其池化的实现。当在项目中大量使用 go关键字启动 goroutine时可能会引发一些问题:
- 协程数量过多:虽然
golang官方号称go可以调度百万级goroutine,但是其带来的性能影响和内存占用是不可控的 - 协程泄露:如果协程在执行过程中出现了
bug,导致无法被GC回收,当存在大量goroutine无法被回收时可能导致程序panic
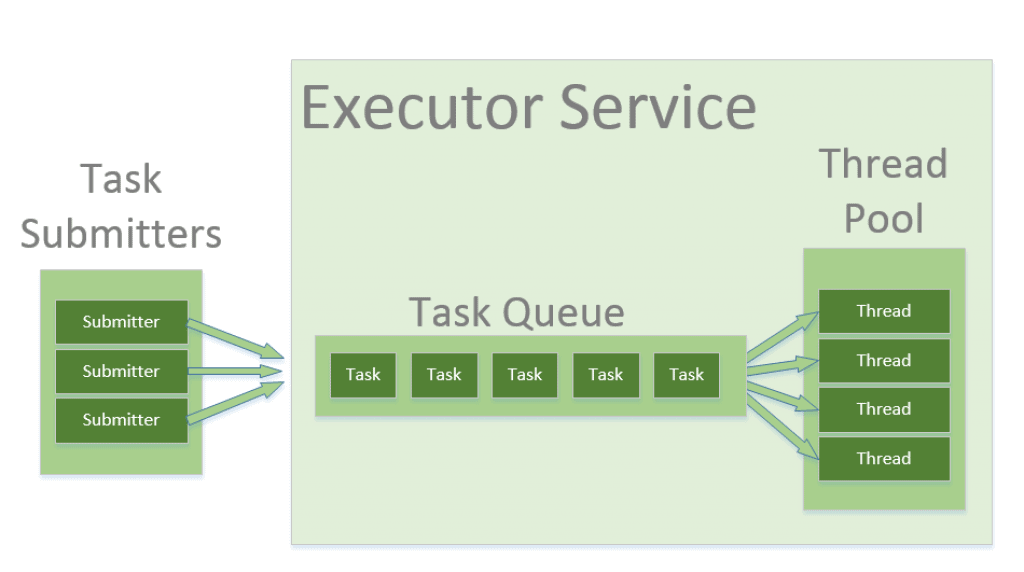
在此基础上,字节跳动开源了其协程池实现,原理类似于 Java的线程池,使用链表来记录待处理的任务信息,同时使用 sync.Pool将对象池化,减少内存分配操作。
Github地址
目录结构
# gopkg/util/gopool
config.go # 参数配置
gopool.go # 入口文件 对外暴露函数
pool.go # 协程池接口和实现
pool_test.go # 单元测试
worker.go # 工作协程
config.go
package gopool
const (
// 默认阈值
defaultScalaThreshold = 1
)
// Config is used to config pool.
type Config struct {
// 启动工作协程的待处理任务阈值
ScaleThreshold int32
}
// 创建一个默认配置
func NewConfig() *Config {
c := &Config{
ScaleThreshold: defaultScalaThreshold,
}
return c
}
pool.go
package gopool
import (
"context"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
)
type Pool interface {
// 协程池名称
Name() string
// 设置工作协程数量限制
SetCap(cap int32)
// 提交任务
Go(f func())
// 提交任务并传递Context
CtxGo(ctx context.Context, f func())
// 设置协程在运行过程中发送panic的处理逻辑 会传递提交任务时的Context和panic信息
SetPanicHandler(f func(context.Context, interface{}))
// 返回当前正在运行的工作协程数量
WorkerCount() int32
}
// 任务对象池
var taskPool sync.Pool
func init() {
taskPool.New = newTask
}
// 任务链表 用于存储提交任务的Context和函数
type task struct {
ctx context.Context
f func()
next *task
}
// 清空字段
func (t *task) zero() {
t.ctx = nil
t.f = nil
t.next = nil
}
// 清空字段后将任务放回对象池
func (t *task) Recycle() {
t.zero()
taskPool.Put(t)
}
// 创建一个新任务对象
func newTask() interface{} {
return &task{}
}
// 任务链表 未使用
type taskList struct {
sync.Mutex
taskHead *task
taskTail *task
}
// 协程池实现
type pool struct {
name string
cap int32
// 配置信息
config *Config
// 链表的头节点
taskHead *task
// 链表的尾节点
taskTail *task
taskLock sync.Mutex
taskCount int32
// 当前的工作协程数量
workerCount int32
// pacnic处理函数
panicHandler func(context.Context, interface{})
}
// 创建协程池
// name 协程池名称
// cap 工作协程限制数量
// config 配置信息
func NewPool(name string, cap int32, config *Config) Pool {
p := &pool{
name: name,
cap: cap,
config: config,
}
return p
}
func (p *pool) Name() string {
return p.name
}
func (p *pool) SetCap(cap int32) {
atomic.StoreInt32(&p.cap, cap)
}
// 提交任务 调用CtxGo传递一个空Context
func (p *pool) Go(f func()) {
p.CtxGo(context.Background(), f)
}
// 提交任务 最终调用的方法
func (p *pool) CtxGo(ctx context.Context, f func()) {
// 从任务对象池中拿到一个空的任务对象
t := taskPool.Get().(*task)
// 设置字段
t.ctx = ctx
t.f = f
// 加锁 开始操作任务链表
p.taskLock.Lock()
// 如果链表的头节点为空 就说明当前任务是第一个任务
// 设置链表的头节点和尾节点都为当前任务
if p.taskHead == nil {
p.taskHead = t
p.taskTail = t
} else {
// 如果不为空 就将当前任务设置为链表的尾节点
p.taskTail.next = t
p.taskTail = t
}
p.taskLock.Unlock()
// 将待处理的任务数量加1
atomic.AddInt32(&p.taskCount, 1)
// 判断当前是否符合启动工作协程的条件
// 1. 待处理的任务数量大于等于启动工作协程的阈值
// 2. 当前正在运行的工作协程数量小于工作协程数量限制
// 如果正在运行的工作协程数量等于0 那么会直接运行
if (atomic.LoadInt32(&p.taskCount) >= p.config.ScaleThreshold && p.WorkerCount() < atomic.LoadInt32(&p.cap)) || p.WorkerCount() == 0 {
// 添加工作协程数量
p.incWorkerCount()
// 从对象池中拿到工作协程对象
w := workerPool.Get().(*worker)
w.pool = p
// 运行工作协程
w.run()
}
}
// SetPanicHandler the func here will be called after the panic has been recovered.
func (p *pool) SetPanicHandler(f func(context.Context, interface{})) {
p.panicHandler = f
}
func (p *pool) WorkerCount() int32 {
return atomic.LoadInt32(&p.workerCount)
}
// 添加工作协程数量
func (p *pool) incWorkerCount() {
atomic.AddInt32(&p.workerCount, 1)
}
// 减少工作协程数量
func (p *pool) decWorkerCount() {
atomic.AddInt32(&p.workerCount, -1)
}
worker.go
package gopool
import (
"fmt"
"runtime/debug"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
"github.com/bytedance/gopkg/util/logger"
)
// 工作协程对象池
var workerPool sync.Pool
func init() {
workerPool.New = newWorker
}
type worker struct {
pool *pool
}
func newWorker() interface{} {
return &worker{}
}
// 运行方法
func (w *worker) run() {
// 使用 go 启动一个goroutine
go func() {
// 循环执行任务链表中的所有任务
for {
var t *task
// 开始任务链表所
w.pool.taskLock.Lock()
// 如果链表中存在任务
// 那么就取出一个任务并且将链表头往后移一个节点
// 同时再将协程池中的待处理任务数量减1
if w.pool.taskHead != nil {
t = w.pool.taskHead
w.pool.taskHead = w.pool.taskHead.next
atomic.AddInt32(&w.pool.taskCount, -1)
}
// 如果获取倒的任务为空
// 说明待处理任务链表中所有的任务都已经被执行
// 那么就关闭当前工作协程并回收对象并跳出循环
if t == nil {
// if there's no task to do, exit
w.close()
w.pool.taskLock.Unlock()
w.Recycle()
return
}
w.pool.taskLock.Unlock()
// 再启动一个func用于任务执行
// 如果不启动func 当任务执行出现panic时 会跳出循环并结束当前方法
func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
// 判断是否设置了panic处理函数 如果设置了就调用
if w.pool.panicHandler != nil {
w.pool.panicHandler(t.ctx, r)
} else {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("GOPOOL: panic in pool: %s: %v: %s", w.pool.name, r, debug.Stack())
logger.CtxErrorf(t.ctx, msg)
}
}
}()
// 执行任务函数
t.f()
}()
// 回收任务对象
t.Recycle()
}
}()
}
// 关闭任务协程 减少协程池中工作线程的数量
func (w *worker) close() {
w.pool.decWorkerCount()
}
func (w *worker) zero() {
w.pool = nil
}
func (w *worker) Recycle() {
w.zero()
workerPool.Put(w)
}
gopool.go
package gopool
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"math"
"sync"
)
// 默认协程池
var defaultPool Pool
// 协程池缓存
var poolMap sync.Map
func init() {
defaultPool = NewPool("gopool.DefaultPool", math.MaxInt32, NewConfig())
}
// 对外暴露的函数 使用默认的协程池执行
func Go(f func()) {
CtxGo(context.Background(), f)
}
func CtxGo(ctx context.Context, f func()) {
defaultPool.CtxGo(ctx, f)
}
// 设置默认协程池的工作协程数量限制
func SetCap(cap int32) {
defaultPool.SetCap(cap)
}
// 设置默认协程池的panic处理函数
func SetPanicHandler(f func(context.Context, interface{})) {
defaultPool.SetPanicHandler(f)
}
// 获取默认协程池正在运行的工作协程数量
func WorkerCount() int32 {
return defaultPool.WorkerCount()
}
// 注册自定义的协程池,将协程池放到 poolMap 缓存中
// 如果协程池的name相同 那么会被覆盖
func RegisterPool(p Pool) error {
_, loaded := poolMap.LoadOrStore(p.Name(), p)
if loaded {
return fmt.Errorf("name: %s already registered", p.Name())
}
return nil
}
// 通过协程池名称获取协程池 不存在返回nil
func GetPool(name string) Pool {
p, ok := poolMap.Load(name)
if !ok {
return nil
}
return p.(Pool)
}




0 条评论